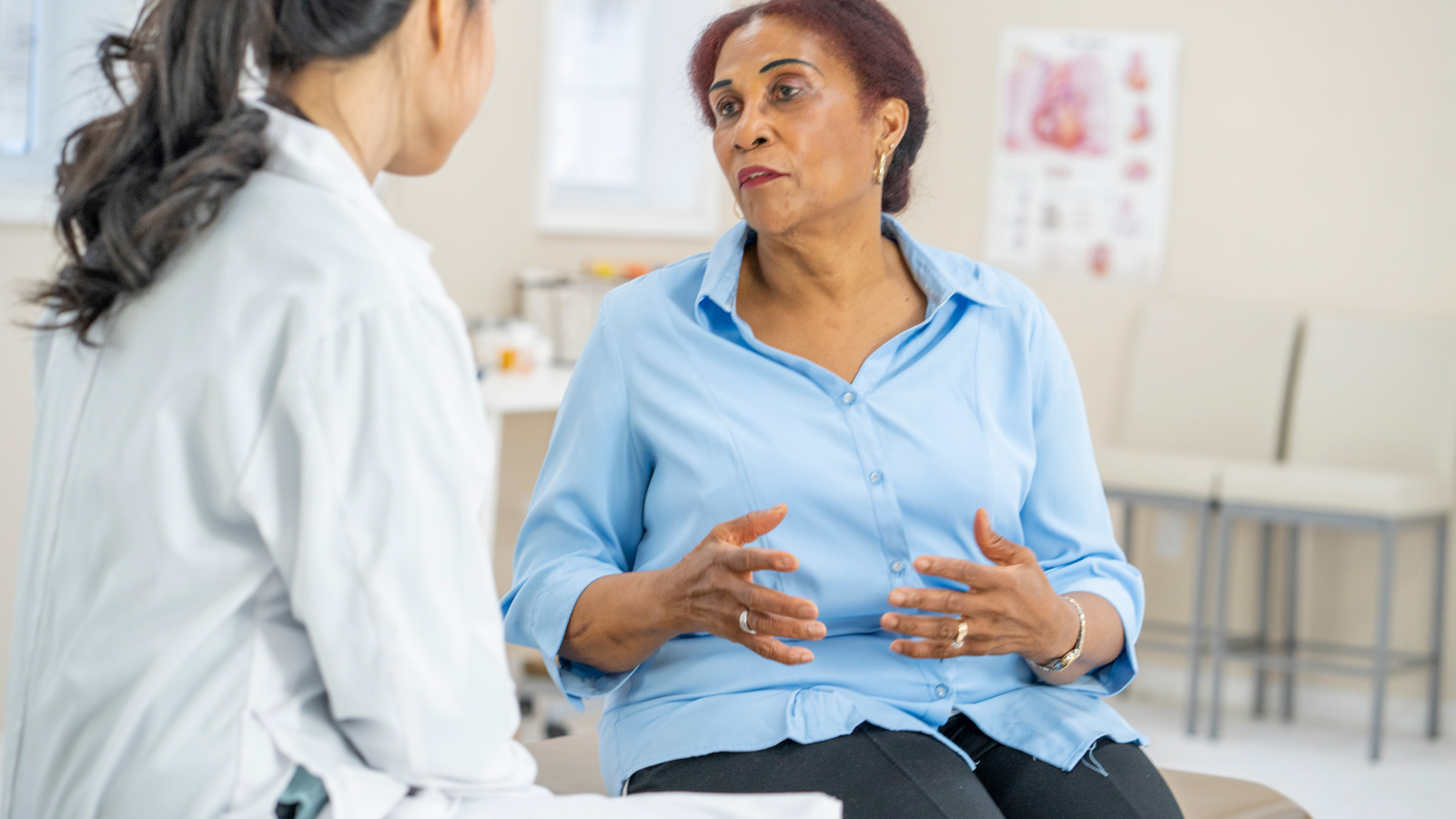
An initial ovarian cancer diagnosis often begins with symptoms, such as bloating or pelvic pain. But ovarian cancer does not always have symptoms in the early stages. Only 20% of ovarian cancers are diagnosed in the early stages. Most patients, between 70% to 80%, have stage III or stage IV ovarian cancer by the time they see a doctor.
A biopsy is the only way to definitively diagnose ovarian cancer. A biopsy removes tissue or cell samples for a pathologist to examine.
What tests detect and diagnose ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is diagnosed through a combination of medical history review, physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. The following tests are currently available to help diagnose ovarian cancer when it is suspected:
Pelvic exam
During a pelvic exam, the doctor feels the uterus, vagina, ovaries, bladder and rectum for any unusual changes in size and shape. The doctor will also feel for an enlarged ovary or signs of fluid in the abdomen. Some cancers are very small before they spread and cannot be reliably detected by pelvic examination.
Imaging tests
Together with a pelvic exam, the following imaging tests may be done to help diagnose ovarian cancer:
- Transvaginal ultrasound – uses a small instrument placed in the vagina to look at the ovaries and uterus. This method is appropriate for people with an increased risk for ovarian cancer or an abnormal pelvic exam.
- CT scan – an x-ray test that makes detailed cross-sectional images of your body. This test is used for those with a concern for ovarian cancer to see if it has spread to other organs.
- MRI – create cross-sectional pictures (not x-rays) of your insides.
- PET scan – a special camera is used to create a picture of areas of the body. The picture from a PET scan is not as detailed as a CT or MRI scan, but it provides helpful information about whether abnormal areas seen on these other tests are likely to be cancer or not. Your medical team will determine if a PET scan is needed and would be helpful.
CA-125 blood test
CA-125 is a protein that can be found in higher levels in people with ovarian/fallopian tube cancer. A CA-125 blood test is an important test, but it does not always mean an individual has ovarian cancer. Some non-cancerous diseases such as endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease can increase CA-125 levels. Also, some ovarian cancers may not produce enough CA-125 levels to cause a positive test. For these reasons, the CA-125 test should not be used as a screening test for those at an average risk for ovarian cancer. Instead, it’s often used to see how well treatment is working, monitor recurrence, and use as a baseline for monitoring those at increased risk of ovarian cancer.
What if my test results come back positive?
If any test returns an abnormal result, it is recommended to see an ovarian cancer specialist, ideally a gynecologic oncologist. They will evaluate the test results and may order other tests to see if there are concerns of cancer.
What to do after an ovarian cancer diagnosis
Getting a diagnosis of ovarian cancer can be overwhelming. Fortunately, there are programs and resources to help. There are also support groups available for patients and caregivers.

Peer Support Programs
Find strength in unity through our peer support groups, connecting you with others who understand your ovarian cancer journey.

Support Services
Explore our support services, designed to empower you through ovarian cancer challenges, reduce barriers to care, and support your journey.
Frequently asked questions
What should I do if I have symptoms of ovarian cancer?
If symptoms do not go away within two weeks following normal interventions such as laxatives, rest, or changing diet and exercise, contact your doctor. Your doctor will look at your medical history, including your family medical history. This will help them learn about any risk factors you might have. Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, including when they started and how long you’ve had them. If your symptoms and medical history suggest ovarian cancer, your doctor will order further testing.
Can a Pap smear detect ovarian cancer?
A Pap smear or test is a common procedure to screen for cervical cancer. It does not detect ovarian cancer.
More information about ovarian cancer diagnosis:
Medically reviewed and updated | December, 2023
Topics




